Abstract: Yueqing Technology continues to invest heavily in the research and development of embodied intelligence design software in the field of embodied intelligence. iRobotCAM fully supports the design of serial and parallel robots, ensuring the correctness of embodied intelligence design from the data source. It supports URDF output and MuJoCo XML output, and supports the application of various simulation and training software such as MuJoCo, ISAAC SIM.
With the development of embodied intelligence, and the improvement of its infrastructure from perception to decision-making, various application scenarios for embodied intelligence are being continuously explored. However, there is a pressing need for a user-friendly design tool that can quickly transform structurally designed models into models based on embodied intelligent robot design standards. This is precisely the reason why Yueqing Technology is dedicated to creating iRobotCAM, a software that can quickly meet the needs of structural design, embodied intelligent design, and simulation.
An embodied robotic end effector is an application scenario, encompassing both humanoid designs with dexterous hands and tool-like end effectors. There’s no inherent superiority or inferiority; it all depends on the needs of the application scenario. The core value of a robot’s end effector lies in whether it provides application capabilities. Taking a robotic gripper as an example, as a typical component in robotic applications, how does iRobotCAM efficiently design a parallel structure of embodied intelligent grippers?
1. iRobotCAM is based on a 3D geometry kernel technology architecture, which can import data formats from various 3D software, including Catia, Solidworks, NX, Creo, Inventor, etc. By importing robot gripper files from Solidworks or Step using multiple files, a 3D structural diagram of the gripper can be created in iRobotCAM.
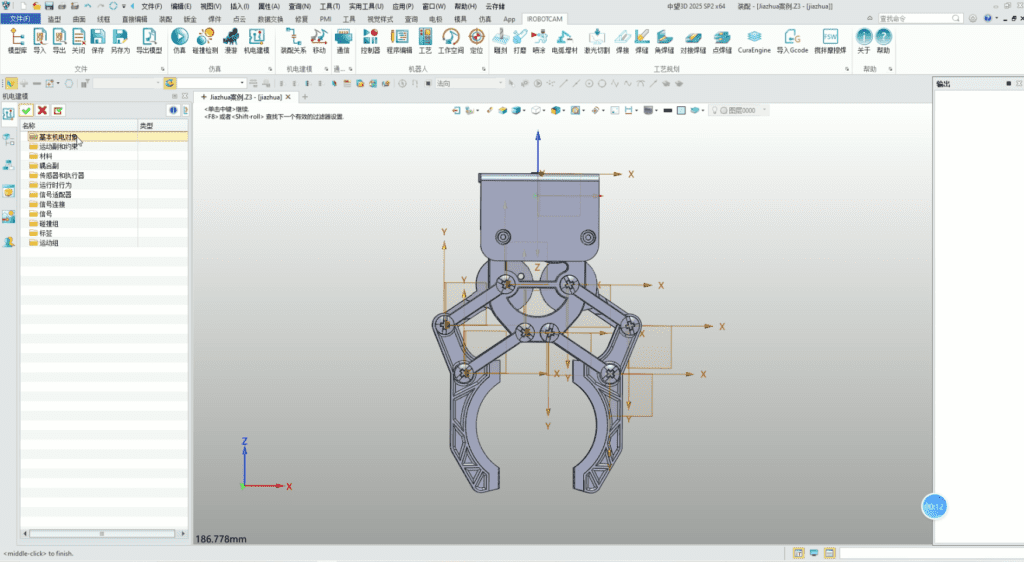
2. Utilizing convenient assembly management functions, material properties for each part can be quickly set, and physical characteristics such as inertia can be calculated.

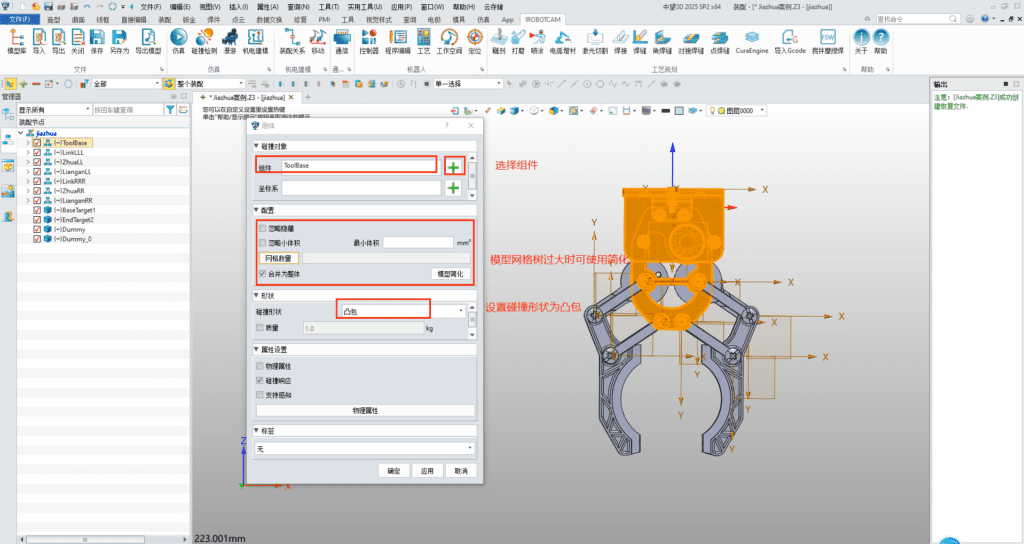
3. iRobotCAM, as a professional robot design and simulation software, utilizes electromechanical design functions to create electromechanical objects and kinematic pairs, including collision detection.
3.1 Creating Rigid Bodies
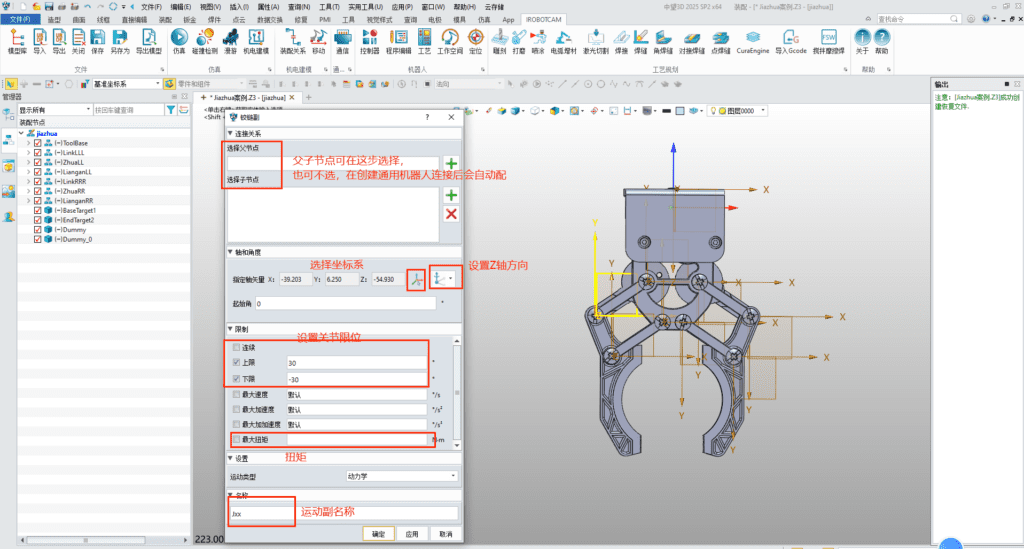
3.2 Creating Kinematic Pairs
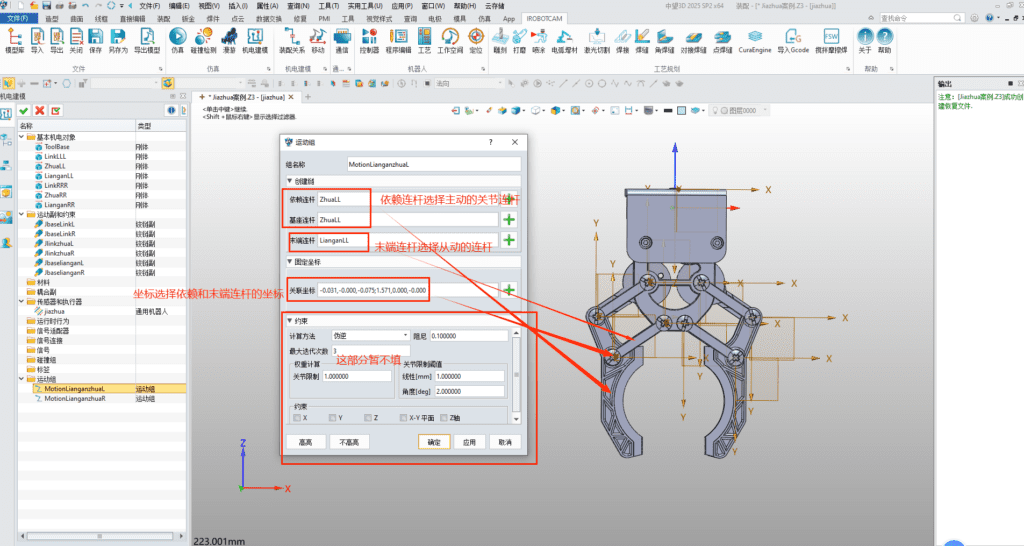
3.3. Creating Exercise Groups
4. By utilizing the convenient skeleton-style robot joint design panel, all joint mechanisms of the robot can be connected to form a complete embodied intelligent general-purpose robot.
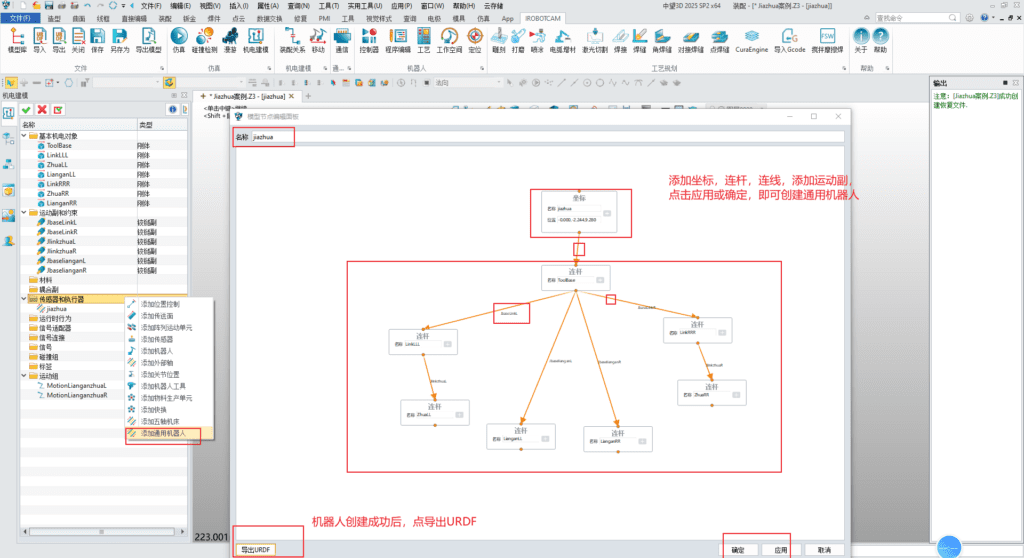
5. Utilizing iRobotCAM’s convenient URDF import and export functions, it can generate universal URDF files or MuJoCo XML files to seamlessly meet the simulation needs of mainstream biomechanical engines such as MuJoCo, Simbody, OpenSim, and Isaac sim.
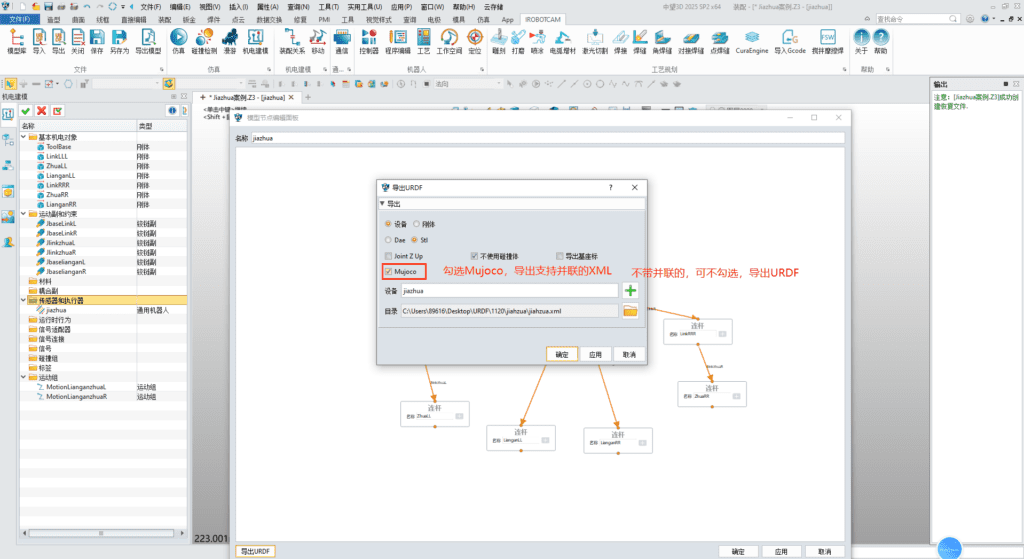

Using the iRobotCAM robot design tool, the design and simulation of parallel robots are no longer cumbersome. At the same time, the structural design of parallel robots can be updated at any time based on the design requirements or simulation data feedback. Through continuous verification of design and simulation, a robot that meets the requirements can be finally formed.
About Yueqing Technology
Yueqing Technology is committed to building an open iRobotCAM robot offline programming platform, which is a digital solution integrating electromechanical conceptual design of production lines, robot processing programming simulation, and virtual debugging.
iRobotCAM website: www.iRobotCAM.com; Contact: cooperation@iRobotCAM.com


